Fayl:Newtons proof of Keplers second law.gif
Newtons_proof_of_Keplers_second_law.gif (390 × 200 piksel, fayl həcmi: 47 KB, MIME növü: image/gif, ilmələnib, 38 çərçivə, 43 s)
Faylın tarixçəsi
Faylın əvvəlki versiyasını görmək üçün gün/tarix bölməsindəki tarixlərə klikləyin.
| Tarix/Vaxt | Kiçik şəkil | Ölçülər | İstifadəçi | Şərh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| indiki | 17:43, 23 iyul 2012 | 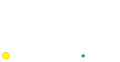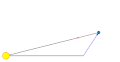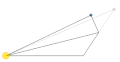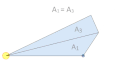 | 390 × 200 (47 KB) | LucasVB | Fixing some swapped labels on A2 and A3, added an extra comparison at the end for A1 = A3. |
| 16:43, 23 iyul 2012 |  | 390 × 200 (43 KB) | LucasVB | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=Isaac Newton's proof of Kepler's second law.}} |Source ={{own}} |Author =Kieff |Date =2012-07-23 |Permission ={{PD-self}} |other_versions = }} [[Category:Animation for ... |
Fayl keçidləri
Aşağıdakı səhifə bu faylı istifadə edir:
Faylın qlobal istifadəsi
Bu fayl aşağıdakı vikilərdə istifadə olunur:
- ar.wikipedia.org layihəsində istifadəsi
- en.wikipedia.org layihəsində istifadəsi
- eo.wikipedia.org layihəsində istifadəsi
- fa.wikipedia.org layihəsində istifadəsi
- he.wikipedia.org layihəsində istifadəsi
- vi.wikipedia.org layihəsində istifadəsi
- vi.wikibooks.org layihəsində istifadəsi


